Create local login for Linux VMs: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Input a Cloud config == | == Input a Cloud config == | ||
During instance creation, there is a | During instance creation, there is a menu called the 'Cloud config'. This is where special commands can be input that will be executed automatically during first boot. Here is an example of a block of commands that can be put into the Cloud config menu to create a local username and password. '''''Remember to update this block with the username and password you want to use. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
#cloud-config | |||
echo | users: | ||
- name: myadmin | |||
groups: sudo | |||
sudo: ['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL'] | |||
shell: /bin/bash | |||
lock_passwd: false | |||
ssh-authorized-keys: [] # Ensure no SSH keys are required | |||
ssh_pwauth: true # Enable password authentication | |||
runcmd: | |||
- echo "myadmin:MyEasyPassword1" | sudo chpasswd # Set password using chpasswd | |||
- sudo sed -i 's/^#PasswordAuthentication no/PasswordAuthentication yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config | |||
- sudo sed -i 's/^PasswordAuthentication no/PasswordAuthentication yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config | |||
- sudo systemctl restart sshd | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
'''''NOTE: The users created with this code block will be able to SSH to your virtual machine (if port 22 is allowed) and have root access. Protect the password carefully! | |||
[[File:CloudConfig.png|border|600px]] | |||
When the instance has been created, you should be able to login to the console (or SSH) with the username/password specified in your Cloud config block. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:09, 28 February 2025
This article will help you inject a local username and password into Linux instances at boot.
Some users prefer to use private keys to grant themselves access to their virtual machines, but some users prefer to simply define a username and password that will allow them to login directly to the console or easily over SSH. With most Linux based operating systems, the process to do this is easy.
Input a Cloud config
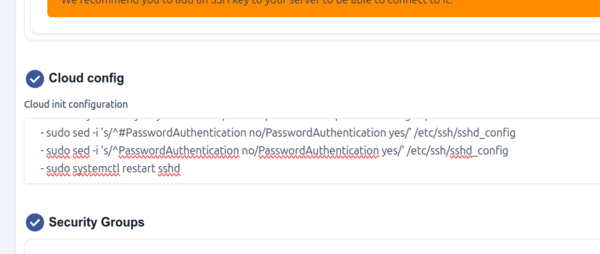
During instance creation, there is a menu called the 'Cloud config'. This is where special commands can be input that will be executed automatically during first boot. Here is an example of a block of commands that can be put into the Cloud config menu to create a local username and password. Remember to update this block with the username and password you want to use.
#cloud-config
users:
- name: myadmin
groups: sudo
sudo: ['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL']
shell: /bin/bash
lock_passwd: false
ssh-authorized-keys: [] # Ensure no SSH keys are required
ssh_pwauth: true # Enable password authentication
runcmd:
- echo "myadmin:MyEasyPassword1" | sudo chpasswd # Set password using chpasswd
- sudo sed -i 's/^#PasswordAuthentication no/PasswordAuthentication yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- sudo sed -i 's/^PasswordAuthentication no/PasswordAuthentication yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- sudo systemctl restart sshd
NOTE: The users created with this code block will be able to SSH to your virtual machine (if port 22 is allowed) and have root access. Protect the password carefully!
When the instance has been created, you should be able to login to the console (or SSH) with the username/password specified in your Cloud config block.